Types of Hydraulic Fluids | Hydraulic Fluid Selection
Types of Hydraulic Fluids
There are different types of hydraulic fluids that have the required properties. In general, while selecting a suitable oil, a few important factors are considered. First, its compatibility with seals, bearing and components is seen; second, its viscosity and other parameters such as fix resistance and environmental stability are also considered. There are five major types of hydraulic flow fluids which meet various needs of the system. These are briefly discussed as follows:
Read More :Functions of Hydraulic Fluids | Specification of Oil
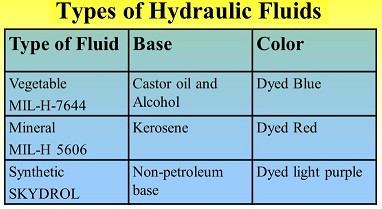
1. Petroleum-based fluids:
Mineral oils are the petroleum-based oils that are the most commonly used hydraulic fluids.
Basically, they possess most of the desirable characteristics: they are easily available and are economical. In addition, they offer the best lubrication ability, least corrosion problems and are compatible with most seal materials.
The only major disadvantage of these fluids is their flammability. They pose fire hazards, mainly from the leakages, in high-temperature environments such as steel industries, etc.
Mineral oils are good for operating temperatures below 50°C, At higher temperatures, these oils lose their chemical stability and form acids, varnishes, etc. All these lead to the loss of lubrication characteristics, increased wear and tear, corrosion and related problems. Fortunately, additives are available that improve chemical stability, reduce oxidation, foam formation and other problems.
A petroleum oil is still by far the most highly used base for hydraulic fluids.
In general, petroleum oil has the following properties:
- Excellent lubricity.
- Higher demulsibility.
- More oxidation resistance.
- Higher viscosity index.
- Protection against rust.
- Good sealing characteristics.
- Easy dissipation of heat.
- Easy cleaning by filtration.
Most of the desirable properties of the fluid, if not already present in the crude oil, can be incorporated through refining or adding additives.
A principal disadvantage of petroleum oil is that it burns easily. For applications where fire could be a hazard, such as heat treating, hydroelectric welding, die casting, forging and many others, there are several types of fire-resistant fluids available.
2. Emulsions:
Emulsions are a mixture of two fluids that do not chemically react with others. Emulsions of petroleum-based oil and water are commonly used. An emulsifier is normally added to the emulsion, which keeps liquid as small droplets and remains suspended in the other liquid.
Two types of emulsions are in use:
Oil-in-water emulsions:
This emulsion has water as the main phase, while small droplets of oil are dispersed in it. Generally, the oil dilution is limited, about 5%;
因此,它表现出水的特征。其局限性粘度差,导致泄漏问题,体积效率损失和润滑性质不佳。可以使用某些添加剂更大程度地克服这些问题。这种乳液用于高位移,低速泵(例如在采矿应用中)。
Water-in-oil emulsions:
Water-in-oil emulsions, also called inverse emulsions, are basically oil based in which small droplets of water are dispersed throughout the oil phase. They are most popular fire-resistant hydraulic fluids. They exhibit more of an oil-like characteristic; hence, they have good viscosity and lubrication properties. The commonly used emulsion has a dilution of 60% oil and 40% water. These emulsions are good for operations at 25°C, as at a higher temperature, water evaporates and leads to the loss of fire-resistant properties.
3. Water glycol:
水乙二醇是一种常用于飞机液压系统的不易燃流体。与矿物油相比,它通常具有低润滑能力,并且不适合高温应用。它具有水和乙二醇,其比例为1:1。由于其性质和空气的存在,它易于氧化和相关问题。它需要添加氧化抑制剂。足够的护理在使用这种流体时是必不可少的,因为它对于某些金属毒性和腐蚀性,例如锌,镁和铝。同样,由于水可以蒸发,它不适用于高温操作。然而,对于低温应用非常好,因为它具有高防冻特性。
4. Synthetic fluids:
Synthetic fluid, based on phosphate ester, is another popular fire-resistant fluid. It is suitable for high-temperature applications, since it exhibits good viscosity and lubrication characteristics. It is not suitable for low-temperature applications. It is not compatible with common sealing materials such as nitrile. Basically being expensive, it requires expensive sealing materials (viton). In addition, phosphate ester is not an environmental-friendly fluid. It also attacks aluminum and paints.
5. Vegetable oils:
The increase in the global pollution has led to the use of more environmental-friendly fluids. Vegetable-based oils are biodegradable and are environmental safe. They have good lubrication properties, moderate viscosity and are less expensive. They can be formulated to have good fire resistance characteristics with certain additives. Vegetable oils have a tendency to easily oxidize and absorb moisture. The acidity, sludge formation and corrosion problems are more severe in vegetable oils than in mineral oils. Hence, vegetable oils need good inhibitors to minimize oxidation problems.
6. Biodegradable hydraulic fluids:
As more and more organizations are understanding their social responsibility and are turning toward eco-friendly machinery and work regime, a biodegradable hydraulic fluid is too becoming a sought after product in the dawn of an environmentalist era. Biodegradable hydraulic fluids, alternatively known as bio-based hydraulic fluids, Bio-based hydraulic fluids use sunflower, rapeseed, soybean, etc., as the base oil and hence cause less pollution in the case of oil leaks or hydraulic hose failures. These fluids carry similar properties as that of a mineral oil–based anti-wear hydraulic fluid, Hypothetically, if a company plans to introduce bio-based fluids into the hydraulic components of the machinery and the permissible operating pressure of hydraulic components is reduced to 80%, then it would inversely lead to a 20% reduction in breaking-out force owing to the 20% reduction in excavator’s operating pressure. It is so because a reduction in the operating pressure of a system leads to a reduction in actuator force.
Besides, the transformation would not only include the cost of fluid and flushing of machinery to transcend from a mineral oil to vegetable oil repeatedly but also include the derating costs of machinery.
Factors Influencing the Selection of a Fluid
The selection of a hydraulic fluid for a given system is governed by the following factors:
1. Operating pressure of the system.
2. Operating temperature of the system and its variation.
3. Material of the system and its compatibility with oil used.
4. Speed of operation.
5. Availability of replacement fluid.
6. Cost of transmission lines.
7. Contamination possibilities.
8.环境条件(闪光,极端气氛如采矿等)
9.润滑。
10. Safety to operator.
11. Expected service life.







